Efficient lightweight sandwich technology for climate-friendly logistics systems
Large load carriers (LLC) offer a lot of storage space with a low dead weight and at the same time a large load capacity. They thus provide important services for global logistics. In a new project, the Fraunhofer Institute for Microstructure of Materials and Systems IMWS, together with Infinex Kunststofftechnik GmbH, HUESKER Synthetic GmbH and TWIN-TEC Packaging GmbH, is pursuing the goal of optimizing large load carriers. By using thermoplastic-based sandwich constructions, they can combine low dead weight, high stability, flexible design and a CO2-saving life cycle.
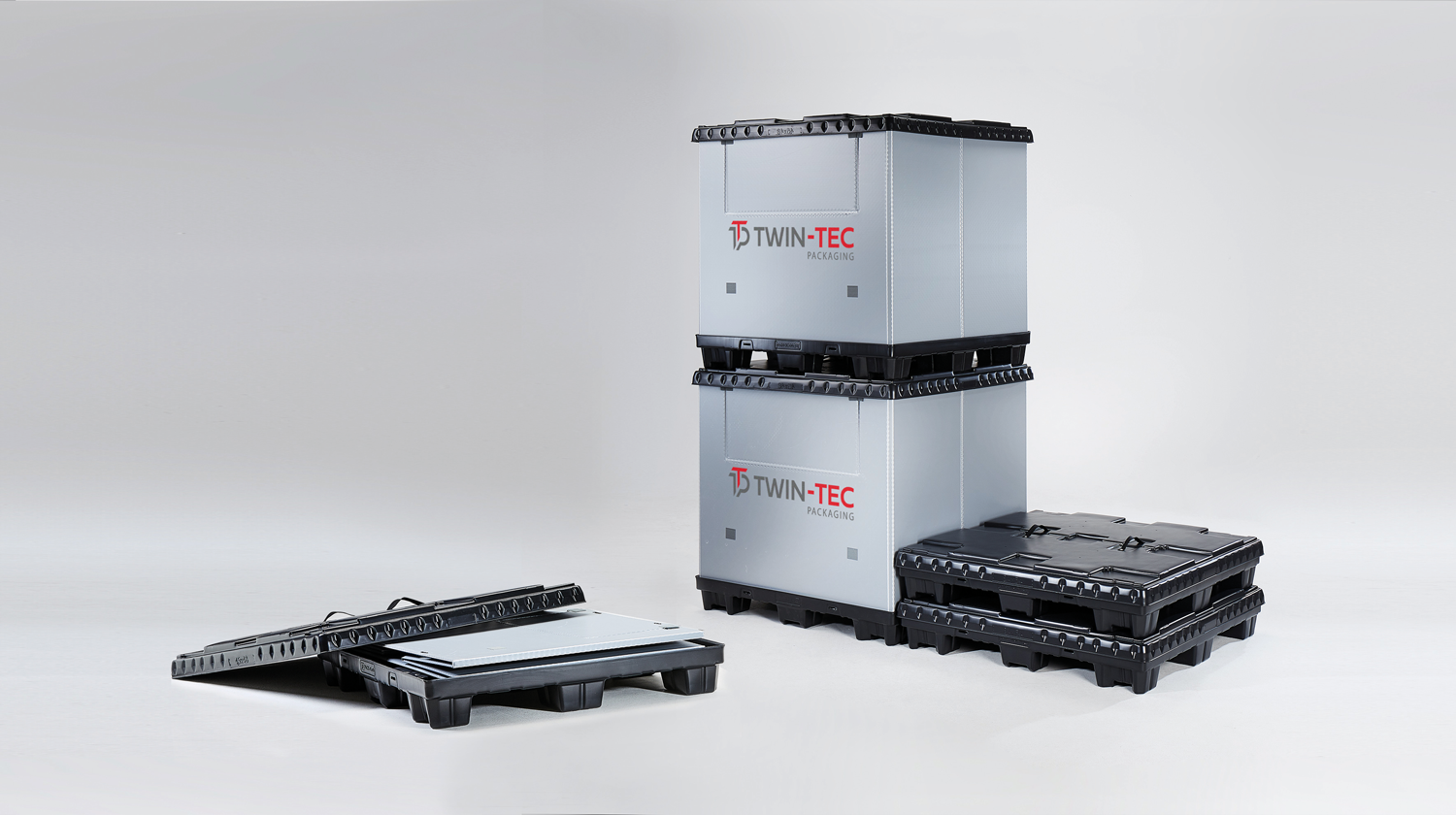


Due to their individual design, large load carriers offer cargo goods special protection and plenty of storage space, especially for heavy and unwieldy goods, machine parts or workpieces. They can be used for both storage and transport, especially for bridging long distances and for weight-critical shipments. Current estimates put the number of large load carriers in use worldwide in the automotive sector alone at more than 2.5 million. At the moment, LLCs in the type of lattice boxes in steel construction are the most established, but due to their design they can neither be used flexibly nor in a space-saving manner.
This is where the consortium steps in and, in the three-year project, pursues the goal of achieving an improved mass-performance ratio for plastic-based large load carriers through the use of a lightweight sandwich construction. "The boxes can minimize their volume many times for empty transport by folding them and stacking them on top of each other. This not only has the positive effect of saving CO2 , but also allows significantly more boxes to be transported in the truck when empty. In addition, the lightweight sandwich construction results in a longer service life for the transport containers," says Sven Wüstenhagen, who heads the project at the Fraunhofer IMWS. The research team also aims to transfer the optimized lightweight LLC to large industrial scale in order to unlock the weight saving potential of the sandwich construction for terrestrial and water-based transport and traffic and to increase material efficiency in additional industries due to the intended transferability of the optimized sandwich constructions.
Optimized design and functional integrations are also expected to reduce the repair rate while increasing load capacity. Another goal is to increase the material recycling rate of fiber-filled thermoplastics. In this way, the plastics used in the LLC can later be reused or recycled in other industries. The Fraunhofer IMWS contributes its expertise in the field of polymer-based fiber composite materials, especially in the area of sandwich structures and the use of materials for lightweight structural design.
Sandwich structures make sense because the combination of two fiber-reinforced cover layers with a lightweight core material enables an excellent ratio between mechanical properties and component weight. Compared with monolithic construction, considerable weight savings of up to 70 percent can be achieved while maintaining the same mechanical performance. If meltable thermoplastics are used for the core and cover layers, flat sandwich semi-finished products can be produced very efficiently in continuous manufacturing processes.
"The findings pursued in the project will potentially open up further innovation paths for large load carriers. In addition to the lightweight construction approach, ways of transporting Li-ion batteries in large load carriers could also be opened up, for example," adds Wüstenhagen.